Experience efficient and practical driving.
Explore the diverse range of all-electric vehicles, including compact cars and SUVs. Enjoy high-torque, long everyday ranges, quiet driving and zero-emission tailpipe driving.


Electric driving technology.
Battery electric vehicles are a good choice for people who want zero tailpipe emissions, quiet and quick acceleration and access to charging facilities.


Smart technology for intelligent driving.
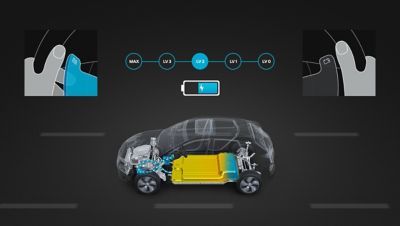
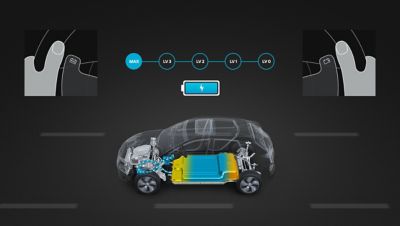
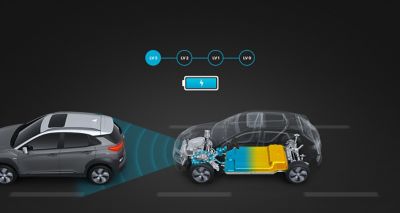
Regenerative braking systems charge the battery by using the electric motor to slow the car – maximising your range.
Charging and driving range.
Charging times and driving ranges can be a concern for drivers. With increased battery capacities and faster charging, electric cars have become a much easier choice, especially when installing a wall box at home or charging at work.
How often do you need to charge?
Set the bar according to your daily commute and calculate the number of days between charges.

KONA Electric
days
IONIQ 6
days
IONIQ 5
days
Just as there is a range of factors that affect the fuel efficiency of an internal combustion engine (ICE), the total electric driving range will be affected by the size of the battery, your driving style, the outside temperature, any passengers you are carrying and more.