Hyundai Worldwide Global Navigation
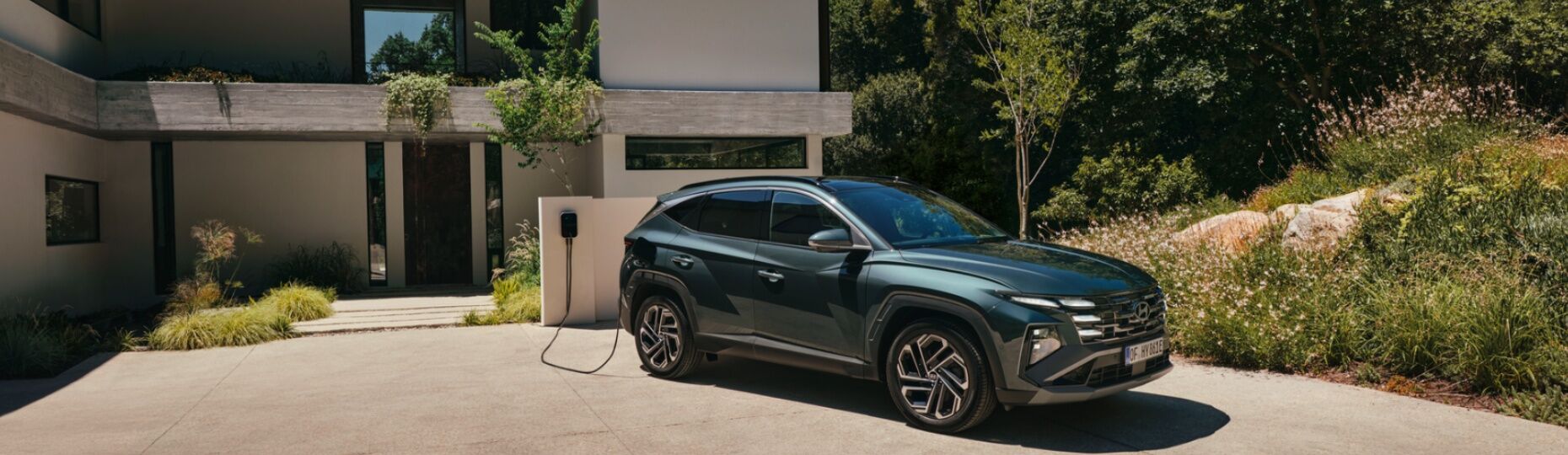


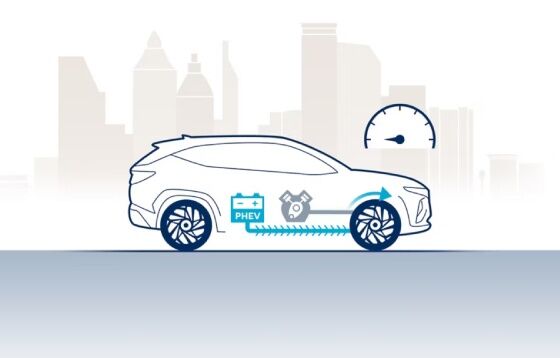
When starting or driving at low speed, the electricity stored in the battery powers the electric motor to accelerate the Tucson Plug-in Hybrid.
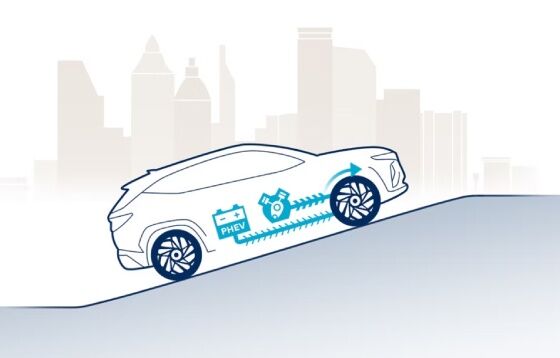
During heavy acceleration or driving uphill, the electric motor and petrol engine work in parallel to maximise acceleration and minimise fuel consumption.
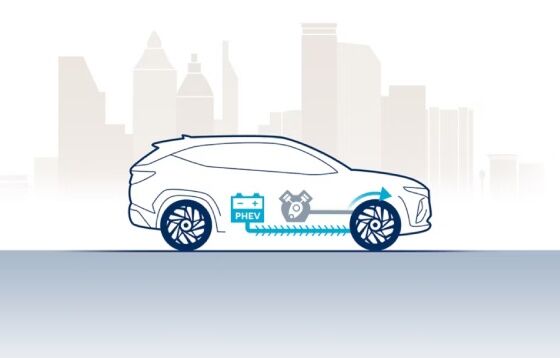
At constant speeds, power is provided by either the petrol engine or the electric motor, whichever is the most energy-efficient in that situation.
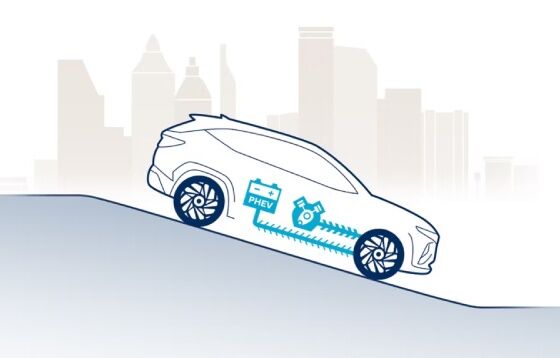
The regenerative braking system charges the battery by using the electric motor to slow the car. When decelerating or driving downhill, the energy generated is stored in the battery.
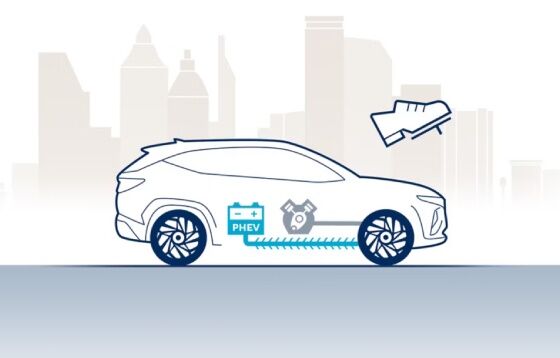
When decelerating (e.g. through braking or when driving downhill) the electric motor operates as a generator and regenerates kinetic energy into electric energy, which is then stored in the battery.