Charge from the comfort of your home.
From discovering our recommended home charger to all the cables and plugs you'll need, find out everything you need to know to be equipped to charge from home in our guide.
Benefits of a wallbox EV charger.
Not only do wallboxes give you the convenience of charging at home, but they have a host of other great benefits too.
Electric car home charging options.
Whilst wall-mounted stations are most common in private homes, stand-alone charging points are great alternatives when wallboxes are not an option or if you wish to change two cars simultaneously.
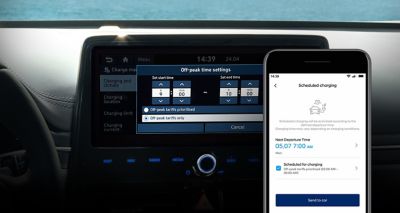
Ohme charging.
The best way to minimise your electric charging costs is to charge at home and Hyundai recommends Ohme as our preferred home electric car charger supplier.
Cables for electric car charging at home.
When charging at home you have two different types of plugs you could use: a type 2 cable, which is typically plugged into a wallbox or an ICCB cable, which is designed for your domestic plug socket.
What factors affect EV charging speeds?
As we've learned, every plug is not created equal - or better said: many factors affect the speed at which your electric car can charge at home, such as the:
- Size and state of charge of the battery
- Max. charging rate of the on-board-charger
- Max. charging speed of the home charger
- External temperatures - batteries do not like extreme heat or cold
Learn more about going electric.
Explore alternatives to home charging or if you're ready take a look at some of our latest electric car offers.