Well established. And future-ready.
From humble beginnings, the technology behind internal combustion engines has developed at an exponential pace, toward more power and torque, but also toward greater efficiency and emission reduction. Hyundai has evolved as a global leader in all of those areas.
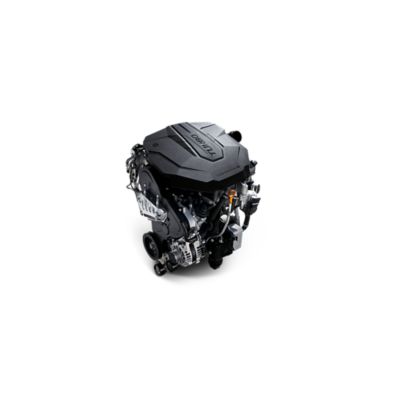
Modern engine technology: Smartstream.
'Smart’ technological objectives of saving fuel, improving performance, and reducing gas emissions were applied to every step of the ‘Stream’ when Hyundai engineers developed our latest powertrain technology: the stream of air and fuel injected in the engine, and its explosive power delivered to the wheels via the transmission.
Smart transmission technologies.
In internal combustion engine vehicles, transmissions serve the important role of situationally adjusting the engine RPM to allow controlled application of power. Appropriate shifting of gears lets the engine continuously function at high efficiency, improving both performance and fuel economy.
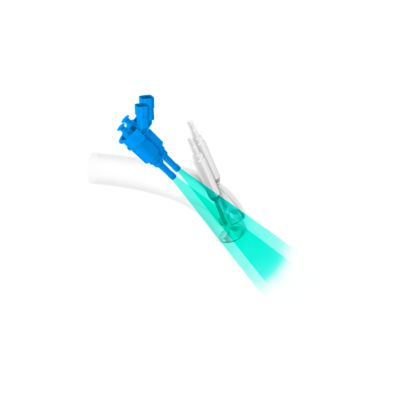
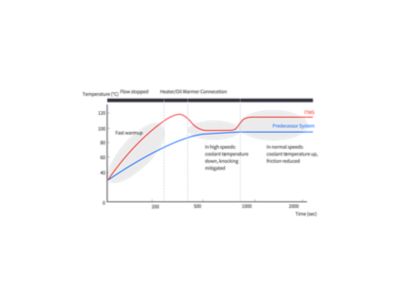
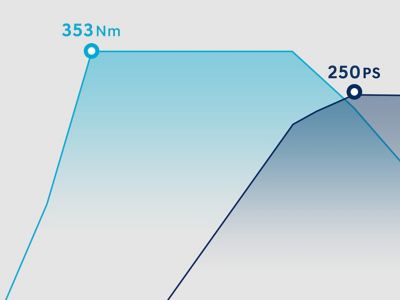
8-speed wet Dual-Clutch Transmission (DCT).
Dual-Clutch Transmissions (DCT) combine the advantages of manual transmission and automatic transmission. Their fast shifting and highly efficient power delivery combines the convenience of automatic with the fuel efficiency of manual transmissions. Wet DCTs use oil to cool the clutches, withstanding the higher torques of our most powerful engines.
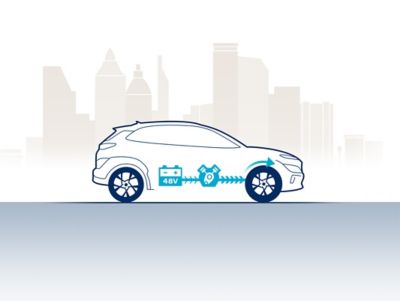
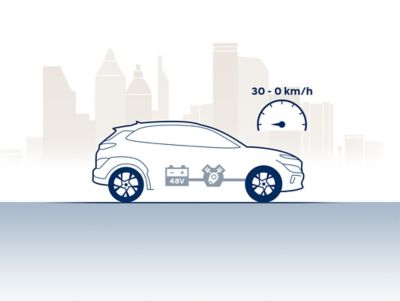
48V mild hybrid.
The 48V mild hybrid powertrain system supports the combustion engine, adding electric power during the different stages of driving. Find out more about this innovative fuel-saving system.


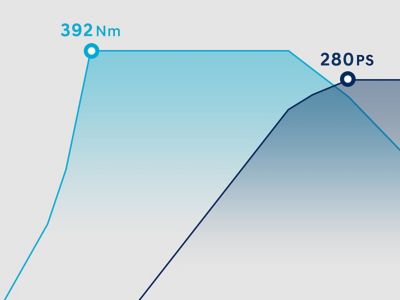
Efficient and powerful: our petrol and diesel engines.
Hyundai offers a wide range of highly efficient and powerful internal combustion engine, which are designed to meet a variety of personal preferences and regulatory guidelines.
Discover more Hyundai powertrains.
From hydrogen fuel cell electric powertrains to electrified engines like a 48-volt mild hybrid, hybrid, plug-in hybrid or an all-electric vehicle, you can find more information here.